
TL;DR: What’s the Meaning of a Virtual Conference & How to Host One (2026)
A virtual conference is an online event where multiple experts deliver live or recorded sessions around a focused theme. It helps you grow your audience, build authority, generate revenue, and create long-term content assets, while giving speakers exposure to new audiences and a platform to promote their products or services.
At Tagoras and Learning Revolution, we’ve been holding virtual conferences regularly since 2017.
Here are a few insights from our experiences.
🧩 How a Virtual Conference Works (Step-by-Step)
– Pick a niche and theme your audience wants to learn about.
– Invite 4–8 speakers who can cover different angles of the topic.
– Break the topic into sessions and align speakers with them.
– Build a registration site using WordPress, WooCommerce, and a conference theme.
– Set up email, Zoom, and community tools (Mailchimp, BuddyBoss, MemberPress).
– Coordinate with speakers: share session ideas, offer content and tech support.
– Promote the event using your list, speaker audiences, and affiliates.
– Host the live sessions, enable networking, and ensure smooth support.
– Record and repurpose all sessions into courses, products, or ongoing marketing.
– Repeat annually or quarterly as a repeatable and scalable business model.
💡11 Practical Tips for Success
– Curate strong context so sessions feel connected, not random.
– Give speakers ready-made promo assets (text, images, links).
– Add social interaction via live chat and post-session discussions.
– Use live video to build connection—don’t rely only on slides.
– Prepare for tech support with a clear plan and a freelance assistant.
– Run content and dry-run calls with speakers before the event.
– Engage attendees as collaborators via Q&A, case studies, and coaching.
– Offer value to sponsors and make them active partners in promotion.
– Use the digital format smartly (spread sessions, prerecord if needed).
– Send frequent reminders—don’t assume people will remember.
– Start planning early (at least 4–5 months out) to get it right.
For detailed tips and examples, read the complete article.
My company, Tagoras, has hosted a virtual conference most years since 2017, well before the COVID surge, and it has become a core part of our business
Through it, we’ve attracted hundreds of new customers, raised awareness among thousands of future prospects, and strengthened our relationships with our most devoted followers.
And, of course, we’ve recorded everything, creating a range of opportunities for new products and content marketing.
In this detailed guide, I’ll share why you should seriously consider the virtual conference business model and how you can implement it effectively.
If you are looking for a virtual conference platform, check out
11 Best Virtual Conference Platforms for Expertise-Based Businesses.
What Is A Virtual Conference
A virtual conference is simply an online event where you bring together experts on a specific topic to deliver talks on one platform. The idea is straightforward: participants get all the knowledge they need in one place, while you, as the host, benefit in multiple ways.
For participants, it’s incredibly convenient. They can access expert insights in a single event without travel or high costs.
For example, our most recent virtual conference was the Leading Learning Summit 2026 where over 30 of the top edupreneurs, e-learning professionals, and thought leaders spoke about all aspects of the online learning space.

For you, as the organizer, the benefits of a virtual event are even greater.
You build valuable relationships with the experts you invite, earn revenue through participant registration fees, and create a goldmine of recorded content that becomes the foundation for future courses, products, and marketing materials.
It’s essentially a business model that pays you to build your network and content library simultaneously.
7 Benefits Of Hosting A Virtual Conference
In addition to the reasons I just highlighted, here are a number of other reasons I think a virtual conference is worth considering, maybe even in advance of creating a course:
- Putting one together makes you a “convener” in your niche, someone who can connect the dots and create value. This is a clear path to elevating your expertise and being perceived as a thought leader.
- You get to showcase your own expertise and you get a chance to associate yourself with other experts, which tends to raise perception of your expertise (especially if some of the other experts are already more established than you are).
- You also get to leverage the marketing power of the other experts you involve to reach a much broader audience than you could reach on your own.
- You get to move fast in putting together an offering. Many of us struggle with putting together a whole course, but any of us can deliver a online session or two in our topic of expertise – and then leverage others to provide additional content.
- As already noted, you can record the whole thing, so you end up with both a live event and a product you can continue to promote and sell afterwards.
- Once you have done it once, it’s repeatable – and it can grow bigger and bigger over time as you attract more attendees. It starts to become a “franchise” that you could actually sell to someone else in the future.
- Last, but certainly not least, you will learn a ton in the process. Chances are very high that you will be able to leverage at least some of this knowledge – and the relationships you create – into new opportunities.
How The Virtual Conference Business Works | 8 Easy Steps
Let me give you a quick overview of how this whole thing works.
You’re the host and your job is to organize a virtual conference on a specific topic – let’s say “Course Creation in the Age of AI” or “How to Thrive as a Course Creator in the AI Age.”
You identify 5-6 speakers who can cover different aspects of this topic, so your conference gives participants complete coverage.
You break down the whole topic into different talks. For example, your opening talk as host covers the challenges and opportunities AI poses to course creators and why they need to adapt.
The first speaker delivers a talk on understanding AI and relevant tools for course creators. Another speaks on the way forward and what the new reality looks like. Each speaker covers a crucial piece of the puzzle.
You connect with these speakers and share your talk ideas with them.
What’s in it for them? They get exposure to your audience, you promote their expertise, and they can promote their own products or services to qualified prospects during their session.
Then everyone promotes the conference, you to your email list, each speaker to their audiences, plus you can get affiliates on board. This creates a marketing multiplier effect.
You handle the technical setup: landing page for registration and payment processing, virtual conferencing software, email sequences for participants, and all the backend systems.
During the event, you record every talk. Afterward, you can offer those recordings as separate products, create courses from the content, or use clips for ongoing marketing. It’s a business model that keeps giving.
Easy right? Here’s a summary of the steps again.
Step 1: Choose your niche and theme. Pick a specific topic you know well and that has an audience willing to pay for expert knowledge.
Step 2: Identify and reach out to 4-8 experts in your field. Don’t worry if you don’t know them personally – most experts are eager to share their knowledge on good platforms.
Step 3: Set up your basic technology stack. You’ll need a website for promotion and registration, an email platform, and a video conferencing tool like Zoom.
Step 4: Create your conference schedule. Plan 2-3 days with multiple sessions, leaving time for networking and Q&A.
Step 5: Build your promotional website with speaker bios, session descriptions, and a clear registration system that processes payments.
Step 6: Launch your marketing campaign. Use your own network, leverage your speakers’ audiences, and utilize social media to drive registrations.
Step 7: Run the live event. Host the sessions, facilitate networking, and ensure everything runs smoothly with backup technical support.
Step 8: Deliver post-event value. Send recordings to attendees and begin planning how to repurpose the content into courses, blog posts, or next year’s bigger event.
The beauty is that each step builds on the previous one, creating a system you can repeat and improve annually.
Read: What is a virtual presentation? Proven tips & common mistakes
Implementing a DIY Virtual Conference
Of course, executing the virtual conference business model may sound daunting, but that is also part of the attraction.
A lot of people don’t go this route because it sounds complex. That means those who are willing to roll up their sleeves and do a little work have a great opportunity.
“But I don’t know enough experts who would do this with me,” you may be saying.
I’ll bet good money you are wrong about that.
Sit down a make a list. You only need a few, and they don’t need to be rock stars. Even if you don’t currently have a relationship, if you are able to present a compelling story, most experts are eager to find good platforms for broadening their audience. Aren’t you?
“But the technology is complex,” may be another argument.
Again, I’d disagree.
Take 1: Partner for Tech
When we ran our first virtual conference in 2017, we struck a deal with a platform and service provider who helped us do everything. That was great – and we were able to do it at no cost because of our industry status – but we quickly realized we could take the reins ourselves.
Take 2: Piece Together a Platform
After that, we moved on to running the whole event with a combination of a WordPress website, a standard email platform, and Zoom.
In fact, here’s the whole rundown of what we used:
- Zoom – We used Zoom to deliver all of the live sessions. We captured the recordings for posting in the event community, which was built with:
- WordPress (Free) – This was the core of the promotional site and the community site for the event. WordPress is open source, so it is free, but we paid for very high quality hosting with WPEngine, a company that specializes in WordPress hosting.
- Keynote Theme – This is the theme we used with WordPress on the promo site. It’s great for highlight sessions and speakers, and it integrates well with WooCommerce, which is what we used to take registration payments.
- BuddyBoss – We had an ongoing community site that we also made use of to support the virtual conference. For that, we use BuddyBoss, which is a very full-featured theme that allows for discussion boards, user profiles, and a variety of social media-like interaction tools. This was also the site on which we posted all of our recordings. We used MemberPress in tandem with BuddyBoss to control access to the recordings and other protected content.
- MailChimp – We already used MailChimp for our e-mail lists, so it made sense for using it to communicate with conference attendees. You can use whatever platform you already use. For most major e-mail platforms there are existing (free or low-cost) plug-ins that will automatically add users once they complete a WooCommerce transaction (and this can be easily done with most other e-commerce platforms as well). We post links to to conference sessions in our community site but also send them out to registrants with Mailchimp.
One other element I’ll mention is that we did get a contractor to help us with day-of support for the conference. We found someone through Upwork who was very good and very affordable.
That’s pretty much it.
Leaving aside the email platform, which you probably already have, all of the technology above costs less than $500.
Our event took place over multiple days, so we tended to spend around $300-$400 on the contract support.
Considering that our registration fees averaged around $400 per individual, we covered those costs with a couple of registrations.
Take 3: The Best of Both Worlds
We hit pause on our virtual conference during COVID because we were so swamped with helping other organizations learn about and host virtual conference. When we relaunched, we rebranded as the Learning Business Summit and also took advantage of the evolved breed of virtual conference platforms that COVID has spurred.
Our choice: HeySummit a platform that pulls together all of the key pieces of a virtual conference into an integrated whole while still giving you a great deal of control over doing things they way you want to.

In general, I’m betting one or all of the above are well within your capabilities, or can be with just a little extra contract help.
How To Host A Virtual Conference (Summit): 11 Tips From My Experience
I’ve launched, hosted, and grown multiple virtual conferences and summits – the Learning Business Summit is the latest – and have learned more than a few lessons worth sharing.
Here are the most important ones.
1. Add strong context to your content
It’s relatively easy to round up a bunch of different presenters, schedule them for Webinars over a couple of days, and call that a virtual conference. The problem with this approach is that the sessions are usually only loosely related, attendees tend to cherry pick, and in the end, very little real learning happens.
If you want to deliver real value and impact when you host a virtual conference – and, as a result, prime your attendees to return for your next offerings – you need to put effort into “curating” the experience in way that helps bring out the value of the content in much the same way that a well-curated exhibit in a museum greatly enhances the value of the objects on display.
For our Learning • Technology • Design™ (LTD) virtual conference, this meant have an overarching theme or “big idea” that drove the event – in our case, that learning is a business, and that excelling as a learning business professional requires a commitment to continuous growth in the areas we have identified in our Learning Business Maturity Model.

To introduce and sustain this theme – and to highlight connections among the sessions and the theme – we hosted an opening “priming” session and a closing “synthesis” session on each day of the conference
The priming sessions – which were 30 minutes in length – were used to highlight one of the major themes or ideas of the conference, tee up the sessions for the day, and comment on some of the ways the sessions interrelated with the each other and with the major theme or idea we presented.
In the synthesis sessions – also 30 minutes each – we challenged attendees to review the day, reflect on what they had experienced, and share some ways in which they were going to take action.
If you would like to explore the concept of curating a virtual conference more, check out my aptly titled post/video on How to Curate a Virtual Conference on the Leading Learning site.
2. Make it easy for others to market
Your best promoters for a virtual conference are the people who have a stake in it. This may include presenters, sponsors, exhibitors, and attendees, just to name a few of the more obvious possibilities.
For this particular conference, we focused on presenters and the vendors who had sponsored one of our other key initiatives. We supplied them with specific language and images they could use in e-mails and on key social media channels like LinkedIn and Twitter (see image further below).
Also, in this case, we did not focus on encouraging attendees to market the event. It’s definitely a focus to consider, though – we just know from a lot of past experience that we would be unlikely to get much of a return on effort with our audience. We have, however, seen this approach work very well with other virtual events. The folks at AssociationSuccess, for example, have gotten a lot of their attendees to share their Surge Events on social media and e-mail through using a platform called Snoball. Definitely worth considering.
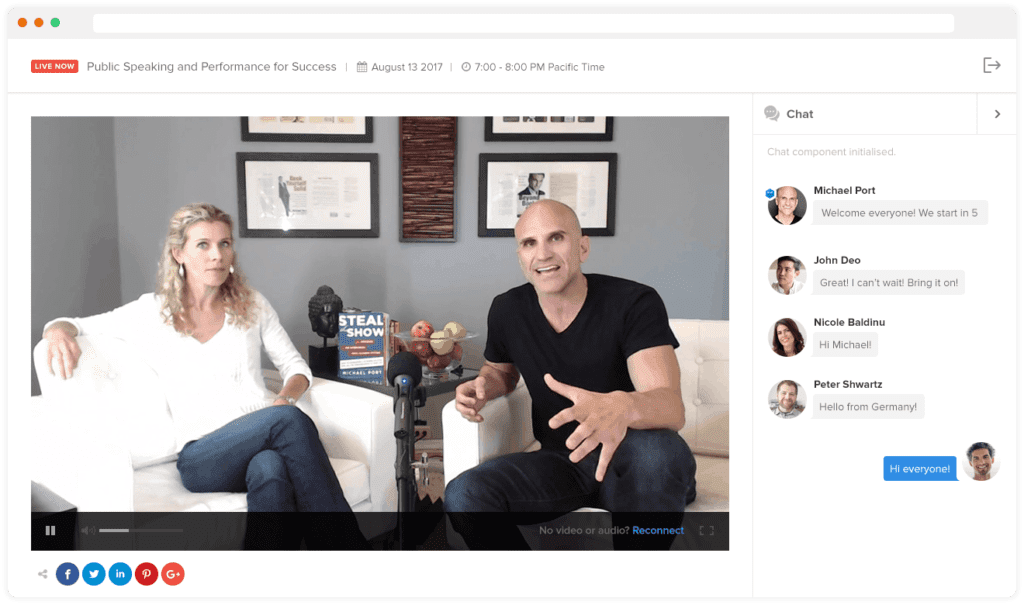
3. Mix in meaningful social
One of the typical criticisms of virtual events is that you don’t manage to get the same networking and interaction that you do with face-to-face events. While it’s true that face-to-face interaction has qualities that don’t translate directly to a virtual environment, the level and quality of interaction you can create online is really quite high – if you put some thought and effort into it.
We used Zoom as our Webinar platform for delivering live sessions. The main reason for that is, at this point, just about everybody and their mother is familiar with Zoom, so we don’t have to give a whole lot of guidance on how to participate in a session and use basic tools like chat – which we put a lot of effort into leveraging effectively during our sessions.
Keep in mind that social interaction doesn’t just happen – at least not initially. You will need to remind people to participate in chat and discussion. I’ve already mentioned that we would continually prompt people to participate in chat during live sessions. For the discussion component in out earlier conferences, we sent out a weekly e-mail in which we highlighted some of the most active discussions on the forum and linked directly to them. The effort definitely paid off: we got hundreds of posts across dozens of topics.
4. Use at least some live video
When I say “live video,” I mean actual human beings in real time on the screen. Not just slides and audio. Not just recorded presentations.
Thanks to platforms like Zoom, streaming video as part of a live Web event has gotten dramatically easier and less risky over the past several years and even just a small amount of video can make an online event feel much more personal and intimate – helping to boost attendee engagement.
We used video for a few minutes at the beginning of all of our sessions just to introduce the speakers – and then we turned it off once the speaker moved into the actual presentation.
We also used video for all of the priming and synthesis sessions mentioned above under “Add some context to your content.” (A still from one of our priming video sessions is included above.) The aim in both cases was simply to make it clear that, while the environment for the learning might be “virtual,” it was filled with real people – people who were there for real teaching, discussion, and learning.
5. Plan for strong customer support
Providing for clear, competent learner support is one of the main ways you can differentiate your event as a professional effort. And, if you want to position it as a premium offering, you definitely need to provide good support.
These days, people are much more accustomed to using the technologies that make a virtual event possible – e.g., Webinars, discussion boards – but that doesn’t mean you won’t run into technical headaches when you host a virtual conference. And, technology aside, you need to make sure that everyone understands all of the event logistics, including what sessions will take place when, where they go to access them, when they can expect recordings to be available. We made sure we posted navigation links to key information in obvious areas of the event Web site, but we also e-mail all attendees multiple times to make sure they knew the session schedule and how to access the sessions.
To help out anyone who did truly needed support, we had a support e-mail address and phone number in the footer of the Web site, a contact page with support information that was linked to as part of the main navigation and – again – we also let attendees know about their support options by e-mail.
Finally, we contracted through Upwork for someone to help us with support during as well as immediately before and after the live sessions. Really, you can find qualified people to do just about anything on Upwork – Fiverr is another great option – and the person we found was very professional and available at a very reasonable rate. We did not actually end up needing much support help – everything went very smoothly – but contract support was valuable to have as an insurance policy (not to mention a stress reducer!).
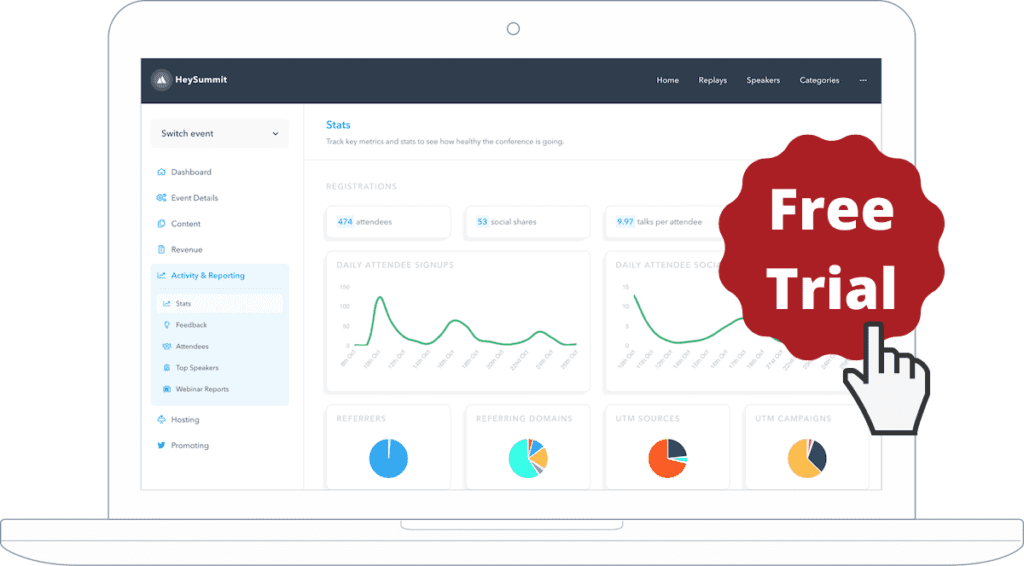
6. Prime your presenters for success
We lined up great leaders for each of our sessions, but we also knew that even the best presenters benefit from good support and opportunities for feedback and practice. So, we made sure from the very beginning – through e-mail and phone calls – that they had a good overall understanding of the event and also that they understood our expectations for their session. We also scheduled two calls with presenters during the weeks before the event.
One of these was what we call a “content call.” In this, we talked through the points the presenter (or, in some cases, presenters) planned to cover during the session and discussed ways we could help make each session as successful as possible. So, for example, we helped some presenters by identifying attendees willing to volunteer marketing or course materials for “diagnosis” during a live session. In another case, we actually collaborated with two presenters to deliver part of a session.
In general, the content call was a way to make sure the presenters had begun actively thinking about their material and that there was enough time for us to help fill any gaps or act on any good ideas that came up.
We also scheduled time for a “dry run” for each session. We did these a week or two before the scheduled time for the session and it gave the session leaders an opportunity to run through as much of their session as they wanted, both to get our feedback and also to make sure they were fully comfortable with the Zoom environment and didn’t run into any issues.
While I can’t say there were no glitches in the LTD sessions, I am certain that the time we spent helping presenters prepare greatly increased the overall quality of the event.
7. Treat attendees as collaborators
I mentioned above that attendees can be valuable collaborators for marketing the event. Through the use of social tools like chat and discussion, they also can and should be valuable contributors to the learning experience. But you can take things even a step or two further by featuring attendees in the session content. We did this in a number of ways.
One I have already mentioned is that we reached out to attendees to volunteer as case studies for some of the sessions. In one of the marketing sessions, an attendee provided a sales page from her organization’s Web site for analysis. For sessions focused on instructional design, one attendee sent in a screen shot from one of his organization’s Webinars, another sent in several screens from a self-paced course that she want advice on reworking.
In addition to leveraging materials submitted by attendees, we also offered “collaborative coaching” sessions. You can read about collaborative coaching process in more detail here, but the general idea is that an attendee poses a challenge or opportunity that she is facing in her learning business, and other attendees – most of whom have face similar challenges – provide advice. You need a certain amount of structure and process to make this work well – which we discuss in the post I just linked to – but the collaborative approach can result in some really great learning interactions.
Finally, we held weekly “Follow Up Friday” sessions which were essentially office hours for addressing questions and discussing any of the content covered in the event. In some of these, we invited attendees to become panelists in the discussion – that is, to join us on video. This brought some fresh faces and perspectives to the discussion

8. Leverage sponsors as partners
Depending on your business, working with vendors as sponsors may not be a part of your current business model. A virtual conference offers a great opportunity to expand into this area.
By “vendors” I mean companies that sell products or services that are of value to your target audience, but that don’t compete with whatever you provide. Ideally, whatever the vendor sells should complement your products or services. In our case, this meant primarily working with learning management system (LMS) vendors, as most of our attendees use or plan to use a learning management system.
Don’t worry if you don’t have a large audience. What most vendors want is a well qualified audience – that is a group of people who clearly possess the characteristics of the vendor’s target customers. If you can offer the chance to get in front of such a group, then you can greatly increase the efficiency of the vendor’s sales process – and that is valuable.
There are a number of ways to monetize this value, from recognizing sponsors (e.g., by displaying their logos) on a page of your event site, to mentioning an linking to them in your marketing e-mails, to giving them an opportunity to lead a session or otherwise speak to your audience during the event. These different approaches should, of course, come with different price tags – an opportunity to speak, for example, is much more valuable than a logo on a Web page.
Keep in mind, though, that revenue is only part of the value of sponsors.
Ideally, you want sponsors to promote the event to their audience, and you my want to incentivize them to do this buy offering some number of complimentary tickets as part of the sponsorship package. Sponsors can also be valuable in identifying, from among their customer base, attendees with relevant stories and case studies to share. And, sponsors may be willing to offer giveaways to some or all of your attendees – and approach that gains exposure for the sponsor and helps to attract attendees. Finally, a sponsor’s brand can be valuable in helping to bolster your own brand and the credibility of the event which, again, helps to attract attendees.
Of course, if you have never worked with sponsors before, getting started can seem a bit daunting. I may need to write a dedicated post on this topic at some point, but some key tips include:
- Determine the benefits you would be able to offer to a prospective sponsors and write these out clearly so that they can be shared with the prospect
- Research other events in your field or industry to see who has sponsored those events. While doing this, also look for any information you can find about typical rates for sponsorship.
- Identify one or more people at the target company who might make decisions about sponsorships. Usually, this is going to be someone in marketing and you can find these people through searching the companies Web site and/or by searching on LinkedIn.
- Ideally, find someone in your personal network with contacts at the target company and use this person as a way connect with whoever you have identified as a potential decision maker.
If you are not able to find a connection through your personal network, but can find a contact either through the Web, LinkedIn, or another source, go ahead and reach out directly. Just make it clear when you do that you have a solid understanding of the contact’s business and that you offer benefits that are highly relevant.
9. Take advantage of the medium
In many ways a virtual conference can and should mirror what happens at a face-to-face conference. By having elements like keynote presentations, breakouts, and opportunities for networking, you’ll align with learner expectations and increase the chances that they will take a chance on a virtual event.
That said, don’t overlook the opportunities that using a digital medium can provide when you host a virtual conference.
For example, we scheduled our most recent virtual event to take place over the course of a full month, with shorter sessions scheduled for an hour on Tuesdays, longer workshops and the above mentioned priming and synthesis sessions spanning four hours on Thursdays, and Follow-up Friday sessions – also mentioned above – taking place for an hour each Friday from 12:30 to 1:30 ET.
While this approach can be a somewhat harder sell for some prospective attendees, it also has strong advantages, including:
- By spacing out the learning over a longer period, there is a much greater chance that your attendees will have the opportunity to digest, review, reflect, and apply what they learn – particularly if you take steps to help facilitate these actions. The end result is that the event will have a much greater impact, greatly increasing the chances that you will have satisfied customers who keep coming back for more.
- It gives you more time to actively engage with your learners in a meaningful way, helping you to build deeper, long-term relationships.
- It gives you some breathing room in planning, enables you to learn and adjust over the course of the event, and relieves some of the pressure for getting everything right in a single 1-3 day period.
- It can greatly increase the chances that attendees will make use of discussion boards. In the first place, they simply have more time. In the second place, they are almost certain to have more questions and comments related to the content as a result of the spacing effect suggested in bullet one above.
Each of these advantages is difficult, if not impossible to achieve with traditional face-to-face conferences. (And most of them align directly with supporting adult learning principles.)
Another key area where virtual conferences provide an advantage over face-to-face is in the ability to pre-record sessions. Overall, we have not made a lot of use of this capability, but we did run into the need to pre-record one of our sessions when the speaker had a last minute conflict. We were then able to play the recording during the scheduled time for the sessions and one of the speaker’s colleagues stepped in to help with handling real-time Q&A for the sessions.
We’re seen other virtual conferences make much more extensive use of pre-recorded sessions, usually with a similar approach to what I just described – they still play the sessions at a scheduled time, but then have real-time chat and Q&A to go along with it. This approach is very often just as effective as having the presenter deliver in real time, and it can give you a lot of control over session length and quality.

10. Don’t skimp on reminders
One of the big advantages of a face-to-face conference is that the attendees are essentially “captive.” Yes, they can skip out on sessions if they need to, but the fact that they are physically present greatly increases the chances that they will participate in most of the experience.
Obviously, this isn’t the case when you host a virtual conference. Even if people have paid to attend, “life” often interferes and participation in the event may take a back seat to demands from customers, co-workers, and other priorities. Moreover, the availability of session recordings – which most virtual conferences can and should offer – makes the “I’ll watch it later” excuse possible (and, of course, they rarely do watch it later).
While there is no way to get rid of this issue entirely, one of the most effective ways to combat it is to make sure you send out frequent reminders. This includes e-mail reminders of upcoming sessions, reminders to participate in discussion forums, reminders that recordings have been posted – basically anything that helps to keep the event top of minds and draw attendees back into the experience.
It is, of course, possible to over do it and annoy attendees with too much e-mail, but my recommendation would be to err on the side of annoyance.
Your attendees did, after all, sign up to attend and – particularly if they paid a registration fee – presumably want to benefit from the experience the event offers. I’d much rather have someone tell me that got a little annoyed by the amount of communication than tell me they missed out on parts of the experience because they forgot about it or didn’t know about parts of it.
Bonus Tip #11: Make Time for Everything Above
In my experience, virtual conferences are significantly less risky and time-intensive than many of the alternatives, but that doesn’t mean they are easy and that they don’t take time. If I were to add a tip to the list above it would be “Start well in advance!”
Everything I describe above is doable, even by a solo edupreneur or very small organization or company (we have a staff of 2.5 people), but it does take advance planning to get all of the pieces to line up. (We started about 4-5 months in advance.)
Still, if you are willing to do the planning and roll up your sleeves to tackle the areas I cover above, the chances you will host a virtual conference that knocks your attendees’ socks off are high.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How much should I charge for a virtual conference?
Pricing depends on your audience and content value, but most successful virtual conferences charge between $50 and $400 per ticket. Offering early bird discounts and tiered access can boost conversions. - Do I need to pay speakers to participate in my virtual conference?
Not always. Many experts are willing to speak in exchange for exposure, affiliate revenue, or the ability to promote their own offers. Just make the value clear upfront. - What’s the best time of year to host a virtual conference?
Avoid major holidays and end-of-year fatigue. Late January–March and September–October are often ideal for professional audiences. - How do I keep attendees engaged during multi-day events?
Mix session formats (keynotes, panels, Q&A), use live chat, send daily recaps, and add interactive segments like polls or challenges. - Can I run a successful virtual conference as a solo creator?
Yes. With proper planning, automation tools, and freelance help, many solo edupreneurs have pulled off high-impact summits without a team. - How do I find and vet speakers for my event?
Start with your network, podcast guests, blog contributors, or social media connections. Look for people who already create valuable content and have an active audience. - What kind of backend support do I need during the live event?
At minimum, a tech troubleshooter, a moderator for live chat/Q&A, and someone managing attendee issues (like login or access problems). - How do I handle time zones for a global audience?
Offer session replays, schedule across multiple time blocks, and clearly display all times in both your time zone and a universal format (e.g. UTC or ET). - What’s the best way to monetize the recordings after the event?
Sell them as an all-access pass, bundle them into a mini-course, or use them as bonuses for future offers. You can also gate them with a membership plugin. - How do I track performance and ROI after the event?
Track registrations, revenue, email list growth, session attendance, rewatch rates, affiliate impact, and post-event purchases or upgrades.
Additional resources:
- 20 Virtual Conference Tips for Success (Leading Learning)
- A Why-To and a How-To: Virtual Conferences in the COVID-19 Era (Leading Learning Webinar Recording)
- Engaging Learners in Virtual Conferences: What You Can Try Online (Leading Learning)
- The Essential Guide to Virtual Conference Platforms (Leading Learning)
Table of Contents
Related Posts
7 Steps to Record a Successful Virtual Presentation
How to Host a Virtual Conference – 10 Tips for Success
Getting an Edge with Virtual Events – A Conversation with Michael Doyle